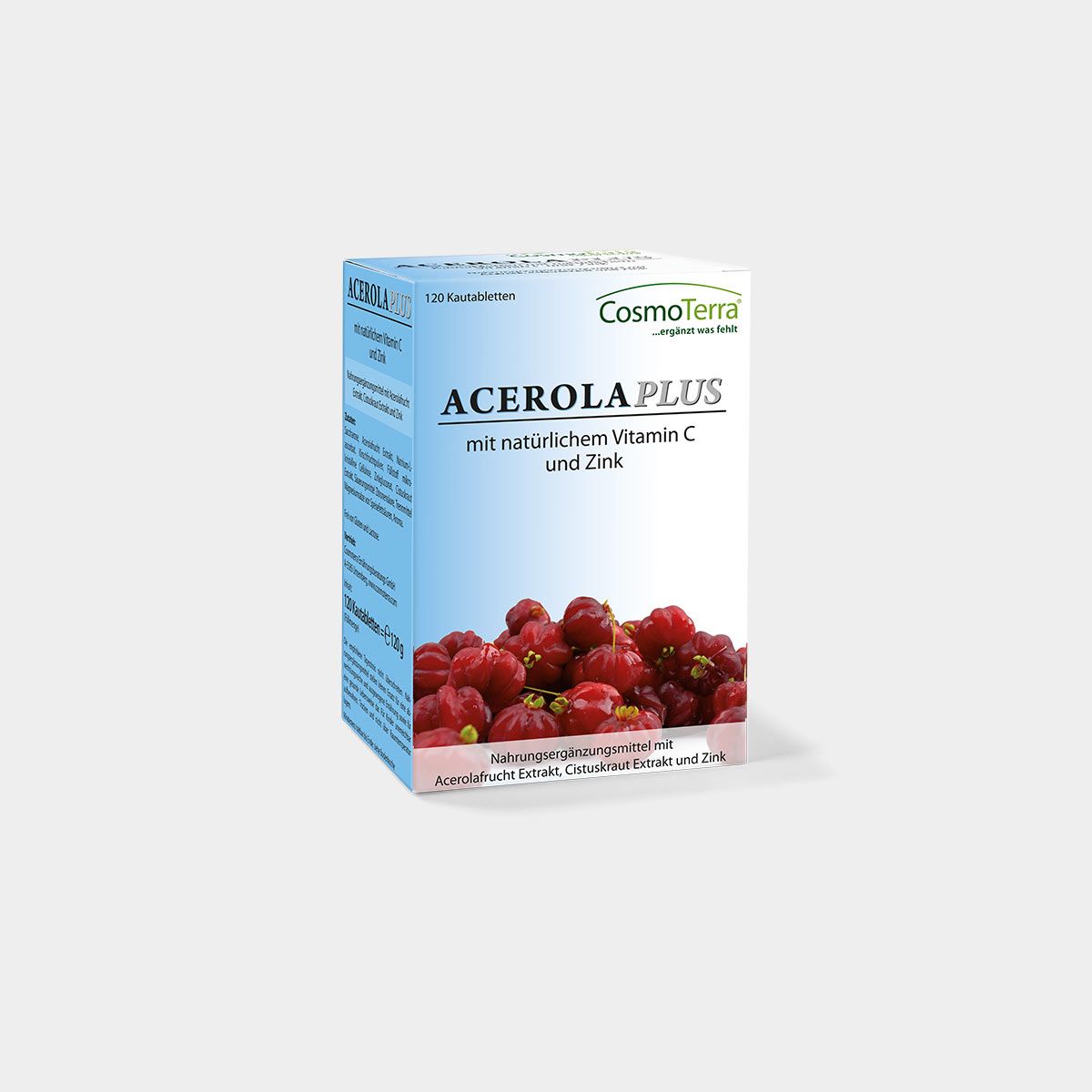
Vitamin C is one of the most important vitamins for strengthening our immune system. Smoking, alcohol, an unbalanced diet, exercise, taking medication, physical and mental stress drastically increase the body’s vitamin C requirements. Vitamin C is responsible for countless biological functions in the body: it delays ageing processes, supports the immune and nervous systems, prevents tiredness and lack of concentration and gives blood vessels elasticity and permeability. Zinc is an elementary trace element for our body. More than 200 different enzymes require zinc as a biological activator. Zinc promotes wound healing, protects cells from oxidative stress, supports metabolic processes in the body and stabilizes the acid/base balance. Acerola cherries have the highest natural vitamin C content of all fruits and vegetables.
One chewable tablet contains more than three times the daily requirement of vitamin C recommended by the European nutritional authorities. This vitamin C was extracted from acerola cherries. In contrast to synthetic ascorbic acid, natural vitamin C is present in its biological precursors and in combination with valuable bioflavonoids. ACEROLA PLUS chewable tablets contain a cistus extract. The cistus plant is considered to be one of the plants with the highest polyphenol content.